It's not only about looking good; protecting your skin from the sun's rays is crucial to your health and wellbeing. Wearing sunscreen every day, rain or shine, is a crucial first step in preventing skin cancer. Select a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least an SPF of 30, since this will provide the most comprehensive protection from both UVA and UVB radiation.
Use it liberally and reapply it every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating, even on gloomy days. Sunscreen is an essential protective layer against the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays, which can cause skin cancer, premature ageing, and sunburn.
Protective gear, in addition to sunscreen, is essential. Cover as much flesh as possible by using lightweight long-sleeved shirts, slacks, and hats. Fabrics that are darker and more closely woven are more secure.
Protecting your eyes from UV radiation and lowering your risk of cataracts is as simple as wearing UV-blocking sunglasses. Also, between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the sun is at its highest, it's best to stay in the shade. Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun by seeking out shade wherever possible when enjoying outdoor activities like hiking or picnicking.
The skin's inherent defence mechanisms are extremely important to know about. Don't let your skin dry out by not drinking enough water. Hydrated skin can better withstand the sun's rays.
Add antioxidants to your diet and skincare products. Sun-damaging free radicals can be neutralised by using antioxidant-rich meals and serums containing vitamins C and E. Restorative sleep and stress management are also critical for healthy skin.
How To Protect Your Skin From The Sun
Shade
Staying in the shade of an umbrella, tree, or other object can help prevent sunburn and skin cancer. Sunscreen and protective gear are your best bets while venturing outside, even when seeking shade.
Clothing
Protect yourself from the sun by donning long sleeves, slacks, or skirts whenever you can. Wear a T-shirt or a beach cover-up instead if you must dress formally. Tightly woven fabric clothing is the most secure option.
While a dry T-shirt will provide greater protection from the sun's rays than a wet one, it's possible that darker colours may be even more effective. The international standards for UV protection have been met by some clothes.
Hat
To keep your face, ears, and the back of your neck out of the sun's rays, choose a hat with a wide brim. If you want to shield your skin from the sun's rays, choose a tightly woven fabric like canvas. Don't wear a straw hat during the daytime. The sun can be avoided more easily if you wear a dark hat.
You should cover your ears and the back of your neck with clothing, use sunscreen, or seek shade if you plan on wearing a baseball cap outdoors throughout the day.
Sunglasses
Wearing sunglasses can help prevent cataracts by shielding your eyes from damaging ultraviolet light. They shield the delicate skin around your eyes from harmful UV rays.
Sunglasses that protect from both ultraviolet A and ultraviolet B rays are optimal. In the United States, this is the norm for sunglasses of all price points. Sunglasses with a wraparound frame are the most effective since they prevent UV light from entering the eyes from any angle.
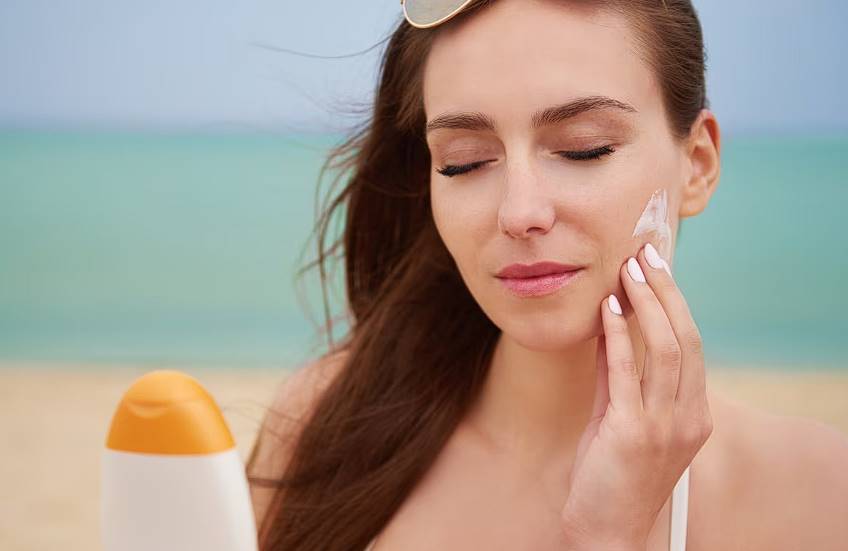
Sunscreen
Before going outside, apply sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, since this will ensure that both UVA and UVB radiation are blocked. Cover every inch of skin that is shown. Seek assistance with areas like your back that are out of reach. Sunscreen is most effective when used in tandem with other measures.
SPF. Sunscreens have an SPF rating that indicates how efficiently they block harmful ultraviolet radiation. A higher score indicates a higher level of safety. A broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15 is recommended.
Reapplication. Sunblock eventually loses its effectiveness. Reapply it every two hours if you're going to be out in the sun, and every time you swim, sweat, or wipe off with a towel.
Date of expiration. Make sure you use a sunscreen that hasn't expired. Without an expiration date, sunscreen should be used within three years. If it has been heated, its storage life will be shortened.

Choose The Right Sunscreen
Sunscreen lotion comes in a variety of SPF ratings.Consider these guidelines while shopping for sunscreen:
Not all sunscreens are created equal, so it's important to check the label before purchasing. Use only broad-spectrum sunscreens, which offer protection from both UVA and UVB rays.
Both ultraviolet (UV) radiation (also known as sunburn) and ultraviolet (UVA) radiation (also known as skin ageing) are damaging when exposed to the sun. 'Broad-spectrum' labels are only given to products that have passed rigors tests.
Make sure the sunscreen you buy has an SPF of 30 or more. The higher the SPF number, the more protection you will have from harmful UVB rays. Sunscreens with SPF 30+ block out 97% of UVB rays, and those with SPF 50+ block out 98%. There is no such thing as a 100% effective sunscreen.
Water-resistant sunscreen is the best choice for use in and around water. Since no sunscreen is entirely watertight, it must be reapplied at regular intervals as directed by the manufacturer. You'll need to reapply sunscreen every time you dry yourself with a towel if you want to remain protected from the sun.
Application
20-30 minutes before going outside is enough time to adequately apply sunscreen. This will allow the sunscreen to fully absorb into the skin before you go outside. It's better to use a little too much sunscreen than none at all, so don't be stingy. Not using sunscreen at all, or not using it often enough, can cause skin damage from the sun.
Adults should use at least 5ml (one teaspoon) per application, whether it's on a leg, face, neck, arm, etc. As a general rule of thumb, you could apply 35 ml (about seven tablespoons) to your entire body. Larger or taller people may require more, while smaller people may be fine with less. Put sunscreen on any exposed skin, including your face.
Reapplication
To maintain protection from UVA/UVB radiation, reapply sunscreen every two hours or immediately after swimming.
How To Treat Sunburn
Without adequate protection from sunscreen and clothing, sun exposure can cause skin damage. Treating sunburn as soon as it is noticed will help heal the skin and relieve the burning sensation. If you're experiencing pain, try some of these dermatologist-recommended solutions.
Without adequate protection from sunscreen and clothing, sun exposure can cause skin damage. Treating sunburn as soon as it is noticed will help heal the skin and relieve the burning sensation. Get out of the sunlight immediately, preferably inside.
Once inside, try some of these recommendations from dermatologists to ease the pain:
- To lessen the discomfort, take chilly baths or showers frequently. When you get out of the shower or bathtub, pat yourself dry lightly, but don't completely remove all of the water. Then, use a moisturiser to further lock in moisture and prevent further loss. The dryness may be relieved by this.
- To relieve sunburn, apply a moisturiser with aloe vera or soy. Hydrocortisone cream, available without a doctor's prescription, may be applied to any location that is very painful. To avoid further skin irritation or an allergic response, avoid using any "-caine" products (such as benzocaine) over sunburn.
- You could try taking some aspirin or ibuprofen to ease the pain and swelling.
- Consume a lot of water. When you get sunburnt, your body pulls fluid to the affected area. When sunburnt, it's important to stay hydrated by drinking extra water.
- Don't pick at blisters; give them time to heal. Second-degree sunburn symptoms include blistering. Blisters form to aid in skin healing and protect against infection, so you shouldn't pop them.
- Sunburnt skin requires special attention during the healing process. When going outside, cover up as much of your skin as possible. We recommend using a tightly woven fabric. The fabric should completely block out light when held up to a strong source.
Sunburn, caused by prolonged exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation, is more serious than it looks and can lead to permanent skin damage. The chance of developing skin cancer rises in response to this damage, making it all the more important to take precautions against sun exposure.

Risk Factors For Harmful Effects Of Uv Radiation
It is important for people of all skin tones to take precautions against the sun's harmful rays. Take extra precautions if you have:
- light-colored skin
- Redheads, blondes, and light browns
- been through skin cancer treatment
- a member of the family who has battled skin cancer
Enquire with your doctor about appropriate sun protection measures if you are taking any drugs. Sun sensitivity may be exacerbated by some drugs. Up to 80% of the sun's ultraviolet radiation can penetrate clouds, even on cloudy days. Make use of the shade whenever feasible.
The Food and Drug Administration is dedicated to guaranteeing the availability of high-quality sunscreens that do not pose any health risks to users. The FDA has proposed a new requirement that all sunscreen products with an SPF value of 15 or higher must be broad spectrum, with increasing broad spectrum protection as the SPF value increases.
This is due to the growing body of scientific evidence linking UVA exposure to skin cancers and other harms. In addition to increasing the maximum suggested SPF value from SPF 50+ to SPF 60+, the FDA proposed revisions to the labelling of SPF values to make it easier for customers to compare and purchase sunscreen.
Conclusion
It is very important for your health and well-being to protect your skin from the sun's harmful effects. One way to stop skin cancer is to wear sunscreen every day, even when you're inside. If you want full protection from both UVA and UVB rays, choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least 30 SPF.
It is also important to wear protective gear like hats, lightweight long-sleeved shirts, and pants. Sunglasses that stop UV rays will protect your eyes from damage and lower your risk of getting cataracts.
Keeping your skin out of the sun is easy if you stay in the shade, wear long arms, pants, or skirts, and clothes that are tightly woven. Hats with a wide top and a tight weave, like canvas, can help protect your face, ears, and the back of your neck from the sun. The best sunglasses are ones with frames that go all the way around your face.
Cover all of your skin with sunscreen that has an SPF of at least 15 before going outside, and get help with places like your back if you need it. Every two hours, especially after swimming or running, put on more sunscreen. Sunscreen must be used within three years of its expiration date in order to keep working.
There are different SPF ratings for sunscreen lotion, and it's important to pick the right one for your face. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays, which are harmful when they hit your skin. Screens with at least 30 SPF stop 97% of UVB rays, and those with 50 SPF or more stop 98%. Sunscreen that doesn't get washed off easily should be used in and around water, and it needs to be reapplied often.
You should put it on 20 to 30 minutes before going outside, and adults should use at least 5ml each time. It is suggested that you reapply it every two hours or right after swimming. As soon as you notice you have a sunburn, you can treat it.
Cold baths or showers, aloe vera or soy moisturiser, hydrocortisone cream, aspirin, or ibuprofen can all help. When you have a sunburn, it's important to stay hydrated, and you should let blisters heal. Wear clothes that are tightly knit and cover up as much skin as you can when you go outside.
Long-term exposure to UV rays can damage skin permanently and raise the risk of getting skin cancer. All skin tones should protect themselves from UV rays, but people with light skin, redheads, blondes, light browns, who have had skin cancer or who have family members who have had skin cancer should take extra care. If you are taking any medications, talk to your doctor about the best way to protect yourself from the sun.
Content Summary
- Protecting your skin from the sun is vital for health and aesthetics.
- Daily sunscreen application is a cornerstone of sun protection.
- Always opt for broad-spectrum sunscreens to shield from UVA and UVB rays.
- Sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher offer optimal protection.
- Regularly reapply sunscreen, especially after swimming or perspiration.
- Sun's UV rays can cause skin cancer, premature ageing, and burns.
- Complement sunscreen with protective clothing.
- Lightweight long-sleeved outfits offer additional safety against sun exposure.
- Dark and closely woven fabrics provide enhanced sun protection.
- UV-blocking sunglasses are essential for safeguarding eyes from UV radiation.
- Avoid direct sunlight between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when UV rays are most intense.
- Hydration helps the skin resist harmful sun rays.
- Antioxidant-rich diets combat sun-induced free radicals.
- Vitamins C and E in serums neutralise sun damage.
- Ensure consistent rest and manage stress for overall skin health.
- Use shade as a primary defence against sunburn and skin cancer.
- Incorporate protective hats with wide brims for face and neck coverage.
- Dark, tightly woven hats offer superior sun protection.
- Baseball caps might require additional sun protection measures for ears and neck.
- Invest in sunglasses that block both UVA and UVB rays.
- Choose sunscreens based on their SPF ratings and broad-spectrum claims.
- Water-resistant sunscreens are ideal for aquatic activities.
- Sunscreens should be generously applied 20-30 minutes before sun exposure.
- Adults typically need at least 5ml of sunscreen per exposed body part.
- Sunscreens should be reapplied every two hours for continuous protection.
- Expired sunscreens lose their efficacy and should be replaced.
- Different sunscreens offer varying levels of UVB ray protection.
- Sunscreen efficacy is enhanced when paired with protective clothing.
- To treat sunburn, remove yourself from direct sunlight immediately.
- Cool baths and showers can alleviate sunburn discomfort.
- Apply moisturisers with aloe vera or soy for sunburn relief.
- Avoid "-caine" products on sunburnt areas.
- Aspirin or ibuprofen can reduce sunburn pain and inflammation.
- Hydration is crucial during sunburn recovery.
- Blisters from sunburn should be left untouched to heal naturally.
- Protect healing sunburnt skin by covering up outdoors.
- Cumulative sun damage can increase the risk of skin cancer.
- All skin tones should practice sun protection.
- Some medications can increase sun sensitivity.
- Cloudy days still pose UV radiation risks.
- The FDA ensures the quality and safety of sunscreens.
- Sunscreens with SPF 15 or higher are proposed to be broad-spectrum.
- Higher SPF values correspond to increased broad-spectrum protection.
- The FDA recommends labelling changes for clarity in sunscreen selection.
- A family history of skin cancer requires heightened sun precautions.
- Light-coloured skin, especially in redheads and blondes, needs extra sun care.
- Sunscreen alone isn't enough; combine it with shade and clothing.
- Sunburn today can lead to long-term skin consequences.
- Regular sun protection reduces the risk of permanent skin damage.
- Prioritise sun safety daily to maintain skin health and appearance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Protecting your skin from the sun is crucial because ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can cause various skin problems, including sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. Sun protection helps maintain healthy skin and reduces the risk of these harmful effects.
The best ways to protect your skin from the sun include wearing protective clothing, such as hats and long-sleeved shirts, seeking shade, and using sunscreen. Sunscreen should be applied generously to all exposed skin and reapplied every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, causing premature aging, while UVB rays primarily affect the surface and cause sunburn. To protect your skin from both, use a broad-spectrum sunscreen that provides protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Look for sunscreens labeled as "broad-spectrum" with a high SPF (sun protection factor) rating.
Yes, it is essential to wear sunscreen on cloudy days as UV rays can penetrate clouds and still cause skin damage. Clouds may reduce the intensity of UVB rays, but UVA rays can still reach the Earth's surface. It's important to apply sunscreen every day, regardless of the weather, to ensure continuous protection.
While wearing sunscreen reduces your skin's ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight, it's still possible to get enough vitamin D through a balanced diet and supplements if necessary.
It's crucial to strike a balance between protecting your skin from the sun's harmful effects and maintaining adequate vitamin D levels. If you have concerns about vitamin D deficiency, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.