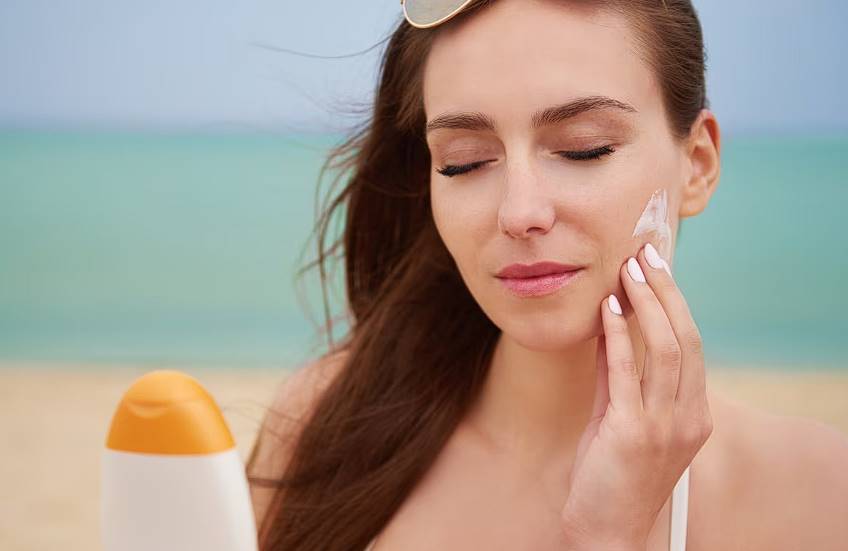
It goes without saying that we should all be diligent about applying sunscreen every day, rain or shine. Despite widespread agreement that sunscreen is essential, few people actually use it.
Think about all the times you've forgotten to put on sunscreen before heading outside, whether it was a scorching summer day, a last-minute trip to the beach, or just a random errand. You may be looking to increase your vitamin D intake or trying to stay away from it because you don't think it's all that vital.
In reality, however, there is no end to the arguments in favour of the necessity of using sunscreen every morning. So, we're here to clear up the myths surrounding this essential step in your daily beauty routine and provide an in-depth analysis of sunscreen's functions.
Why Sunscreen Is Important?
As previously said, sunscreen should be applied at the end of your morning skincare routine to protect your skin from harmful ultraviolet radiation. But why exactly do these rays cause so much damage to the skin? Proceed with the dive.

Uva Rays
Ninety-five percent of the sun's rays that reach Earth are ultraviolet A radiation, which is what gives you that summery glow. That's why bed tans employ this form of radiation!
However, that is no guarantee of their safety. Since these UV rays go deep into the dermis and break down collagen, they are to blame for premature aging indicators such as wrinkles, age spots, fine lines, and more.
They have also been linked to an increased risk of developing several forms of skin cancer. Even indoors, your skin can still be damaged by UVA radiation because it can pass through glass.
Uvb Rays
Ultraviolet B radiation (UVB) is the 5% of the sun's rays that reach Earth's surface. They're the primary reason why people get sunburnt when they're exposed to the sun, hence they have another name: the "sunburn" rays.
The harm from these rays is more superficial than that from UVA rays since they don't penetrate as deeply into the skin. In this way, they irritate the skin, resulting in a burning feeling and redness. Sun damage from ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation is most intense between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the sun is highest in the sky and cannot pass through glass.
What's The Difference Between Sunscreen And Sunblock?
When it comes to skin protection, sunblock and sunscreen are two sides of the same coin. Chemical processes in sunscreens turn UV radiation into heat, which the body then radiates. It takes in the sun's rays before they can reach your skin, protecting it against sunburn.
Conversely, sunblock uses mineral compounds to block UV radiation from reaching the skin. Among the most prevalent are titanium dioxide and zinc oxide. Protects the body from harmful UV rays. The white residue this sort of SPF leaves behind is one of the main reasons people avoid using it. However, once applied, sunscreen is invisible.
The majority of sunblocks offer defence against both ultraviolet A and B radiation. Meanwhile, sunblock is typically used to protect against UVB radiation and hence avoid sunburn. Check the label for "broad-spectrum" to see if the product protects against photodamage and sunburn. This means it has been tested against both UVA and UVB rays and shown to be effective.
The Common Signs Of Sun Damage
The truth is that no quantity of tanning is safe, despite the widespread belief that "base tans" are a good way to ease skin into sun exposure. In response to UV light, melanin is produced, causing the skin to darken (tan). Therefore, any degree of tanning is indicative of possible skin injury. The sun's rays can also cause the following skin problems:
- early lines and wrinkles
- skin sagging
- dark spots
- dry, itchy, or burnt skin patches
- discolouration
- noticeable blood vessel
Reasons For Wearing Sunscreen
Here are eleven of the most compelling arguments in favour of year-round sunscreen use:
Protection From Dangerous Uv Rays
We are increasingly vulnerable to the sun's damaging rays as the ozone layer continues to thin. Even though you should get some sun every day for your vitamin D needs, that is no excuse to overexpose yourself. There is a risk of sunburn and skin injury from this radiation. Sunscreens are essential items because they shield you from UV radiation.
Stops Early Ageing
We'd all benefit from skin that seems younger and healthier. This is arguably the strongest argument in favour of regularly applying sunscreen. Spending time in the sun without protection might hasten the aging process. Sunscreen use is a simple but effective preventative measure.
Wrinkles, sun spots, fine lines, photodamage, hyperpigmentation, and dry skin are all things your skin is protected from with this. Regular sunscreen users under the age of 55 had a 24% decreased risk of developing these signs of ageing compared to non-users.
Reduces Risk Of Skin Cancer
Although sunscreen use initially gained popularity for aesthetic reasons, this additional health benefit is certainly welcome. It is important to protect your skin from the possibility of developing skin cancer by using sunscreen regularly. This is the worst form of skin cancer and particularly threatens older women.
Reduces Face Blotchiness
Put on plenty of sunscreen to shield your face from the sun and stop unsightly red veins and blotchy skin from appearing. Acne and other skin problems caused by the sun's rays can be avoided in this way.
Avoids Sunburns
Because sunburns cause the skin to become more translucent, bruising is accentuated. The symptoms, including peeling, redness, swelling, hives, and itching, may come and go repeatedly.
Sunburns are caused by ultraviolet B radiation. Increased skin cancer risk may result from the blisters. Repeated sunburns may increase your risk of developing deadly melanomas.
In addition, when asked whether they had used sun protection the previous time they got sunburnt, 79.6 percent of 4,088 adults said they had. 38.8% of participants applied sunscreen to their exposed face, neck, and chest to shield their exposed skin. One in twenty-nine said they used sunscreen on their bodies, while another nine per cent said they put sunscreen in their makeup.
Prevents Tanning
Getting a good tan is recommended. However, the intense UVB rays from the sun pose a threat to anyone who goes out into it to get a tan. To avoid UVB-induced tanning, use sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30. If you have sensitive skin, reapply sunblock every two hours. Alternatively, apply it after your workout is over, as perspiration may remove the barrier.
Improving Skin Health
Sunscreen shields keratin, collagen, and elastin, three crucial skin proteins. These proteins are essential for maintaining healthy, supple skin. Use sunscreen containing titanium dioxide to prevent UV damage to these proteins and preserve skin health.
Optimal Cosmetic Choice
Sunscreens that also work as moisturisers are now widely available. Apply it and forget about it for a while. Repeated applications are especially important for people with dry or sensitive skin.
A Wide Selection To Choose From
Sunscreen comes in a dizzying array of varieties these days. And the prices are reasonable. Sunscreen recipes made at home can be found online, making them even more cost-effective.
You Might Not Need To Reapply After A Swim
These days, you may find watertight versions of most sun protection products. You may now relax in the pool without worrying about becoming sunburnt.
A Full-Sleeved Dress Is Not As Effective As Sunscreen
A full-sleeved dress is no protection against the sun. Did you know cotton clothing does not protect from the sun, even when dry? Put on lots of sunscreen even if you're not going outside.
How To Choose The Best Sunscreen For Your Skin Type
If you don't want to look like a wrinkled old raisin, you should always wear sunscreen, rain or shine. But how can you know which product is best for you? Keep in mind the following sunscreen information:
Keep The Sun Protection Factor (Spf) In Mind
The SPF of a sunscreen indicates how well it will shield your skin from the sun's UVB radiation. It measures how long you can spend in the sun without being sunburnt while wearing sunscreen. Sunscreens with a higher SPF rating are more effective and last longer.
This means that even if you spend your days inside an office or at home, it is OK to apply sunscreen with an SPF of 30 on your face and other exposed areas. On the other hand, an SPF 50 or greater is suggested if you work or plan to undertake any kind of exercise outside.
What Can Be Done With Spf 15?
Experts recommend applying an SPF of 30 or more for the most effective sun protection possible, although an SPF of 15 can be useful for day-to-day life as it blocks up to 93% of UV rays.
While products with an SPF of 15 or lower do provide some protection from UVB rays, higher SPFs are more effective. Products with an SPF of 30 provide 97% protection while those with an SPF of 50 provide 98% protection.
Broad-Spectrum Defence Is Preferable
Coverage from multiple angles. Sunscreens are a special kind of sun protection product that either absorbs or reflects UV rays. This sunscreen blocks UVB radiation, the kind that causes sunburn, and UVA radiation, the kind that speeds up the ageing process and can cause more serious disorders like skin cancer. So, instead of grabbing a generic sunscreen, opt for a broad-spectrum one.
When You Are Outside, Dress With Proper Sun Protection
While the significance of applying sunscreen before going outside is generally understood, the necessity of wearing sun-protective clothes may be less so. One of the best ways to shield yourself from the sun is to wear clothing covering your skin.
Fabrics for sun protection apparel are engineered to prevent UV light from passing through. Remember that sun protection apparel is still recommended even if you are using sunscreen. This is because sunscreen might wear off during the day, and the skin can absorb it.
Use Water-Resistant Sunscreen
Sunscreen that can withstand water is a must in the summer. Waterproof sunscreens are specially formulated to withstand sweat and water for extended periods. It's now possible to go swimming, kayaking, or have a day at the beach without worrying about the sunscreen washing off. Remember that most waterproof solutions stop working after 80 minutes in the water, so you will still need to go out and reapply it.

Even Those With Darker Skin Tones Should Use Sunscreen
Believe it or not, people of colour must be careful about sun exposure. Unfortunately, the prevalent belief that having darker skin might protect against sun damage is unfounded.
Regular tanning may make your skin less sensitive to redness and burning by increasing melanin production, but the danger of skin cancer and skin ageing is the same for people of all skin tones.
Remember To Reapply Sunscreen
Sunscreen is not designed to last all day with a single application. It may be necessary to reapply every two hours or more frequently depending on your specific circumstances (e.g., time spent outside, skin type, etc.). Sunscreen doesn't need to be reapplied if you're going to be indoors all day after applying it in the morning.
However, you should reapply sunscreen every two hours if you apply it before going outside, participate in water or sweating activities, or spend the entire day outside.
Conclusion
Sunscreen is an important part of your daily skin care practise because it keeps your skin safe from UV radiation, which can be harmful. UVA radiation, which gives you a summery glow, is what causes wrinkles, age spots, fine lines, and even skin cancer to show up early.
Sunburns are mostly caused by UVB rays, which make up 5% of the sun's rays that reach Earth's surface. UVB radiation from the sun does the most damage between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the sun is at its strongest and can't get through glass.
Sunblock and sunscreen are both ways to protect yourself from the sun. Sunscreens change UV radiation into heat, while sunblocks use mineral chemicals to stop UV radiation from reaching the skin. Most sunblocks protect against both UVA and UVB rays, but most people use it to protect against UVB rays and avoid getting sunburnt.
Sun damage isn't safe, and getting a tan isn't safe, either. The sun's rays can cause lines, wrinkles, droopy skin, dark spots, patches of dry, itchy, or burned skin, discoloration, and blood vessels that stand out. Sunscreen can protect you from dangerous UV rays, stop you from getting old too quickly, lower your risk of skin cancer, make your face less red, and keep you from getting a sunburn.
Sunscreen is important for keeping your face healthy and avoiding tan lines. Use sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 to avoid getting a tan from UVB. Sunblock should be reapplied every two hours or after you work out if you have sensitive skin. Sunscreen also keeps skin proteins like keratin, collagen, and gelatine from being damaged by UV rays. People like sunscreens that can also be used as moisturisers, and they are easy to make at home.
Sunscreen comes in different kinds and can be made at home, which makes it cheaper. Most products that protect you from the sun come in watertight forms that let you relax in the pool without worrying about getting a sunburn. Full-sleeved dresses don't work as well as sunscreen, and it's important to get the right kind of sunscreen for your skin.
Sunscreens with a higher SPF number work better and last longer, but sunscreens with an SPF of 15 or less can still be useful in everyday life. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVB and UVA rays, which can cause sunburn and skin cancer.
When you're outside, you should wear clothes that are made to stop UV light from getting through. Sunscreens that don't get wet are important for summer sports, but most of them stop working after 80 minutes in water.
People of all skin tones should wear sunscreen, because getting a tan can make skin less sensitive to heat and burning. Reapply sunscreen every two hours or more often if your skin type or how much time you spend outside makes it necessary.
Content Summary
- Daily sunscreen application is crucial for skin protection.
- Many overlook the importance of wearing sunscreen every day.
- Sunscreen provides defence against harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- UVA rays account for 95% of the sun's radiation reaching Earth.
- UVA rays can lead to premature ageing and skin cancers.
- Windows don't protect against UVA rays; they can penetrate glass.
- UVB rays, making up 5% of the sun's radiation, cause sunburn.
- UVB rays mainly affect the skin's surface and don't penetrate glass.
- Sunscreen and sunblock, though similar, function differently.
- Sunscreens absorb UV rays and convert them to heat.
- Sunblock uses minerals like titanium dioxide to reflect UV rays.
- Check sunblock labels for "broad-spectrum" to ensure UVA and UVB protection.
- A tan indicates skin damage from UV radiation.
- Sun exposure can lead to wrinkles, dry patches, and discoloration.
- Sunscreen offers protection from dangerous UV rays, especially as the ozone layer thins.
- Regular sunscreen use prevents early ageing signs like wrinkles and fine lines.
- Sunscreen significantly reduces the risk of skin cancers.
- It can prevent facial redness and blotchiness caused by sun exposure.
- Sunburns, caused by UVB radiation, increase skin cancer risk.
- Sunscreen prevents tanning due to harmful UVB rays.
- Sunscreen preserves essential skin proteins like collagen.
- Modern sunscreens can also act as moisturisers.
- A diverse range of sunscreens is available to suit different needs.
- Some sunscreens are water-resistant, offering protection during swimming.
- Wearing clothes doesn't replace the need for sunscreen.
- Choose sunscreen based on your skin type and outdoor activities.
- Higher SPF sunscreens offer better protection against UVB rays.
- An SPF of 30 blocks up to 97% of UV rays.
- Broad-spectrum sunscreens offer protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
- Pairing sunscreen with sun-protective clothing is the best defence.
- Waterproof sunscreens are perfect for water activities.
- Dark-skinned individuals also need sunscreen for protection.
- Reapplying sunscreen every two hours is essential when outdoors.
- Sunscreen is the primary line of defence against photodamage.
- Using sunscreen is a proactive approach to skin health.
- Dispel the myth: darker skin tones aren't immune to sun damage.
- Sun-protective clothing doesn't negate the need for sunscreen application.
- Choose broad-spectrum sunscreen for comprehensive UV protection.
- Don't rely on 'base tans'; they signify skin damage.
- Sunscreen is a beauty staple to prevent premature skin ageing.
- Sunscreen can shield from sunburns and the risks associated with them.
- Sunscreen maintains skin's health by protecting essential proteins.
- Combining sunscreen with appropriate attire maximises sun protection.
- Even on cloudy days, UV radiation is present; wear sunscreen.
- Reapply sunscreen post-water activities for continued protection.
- For everyday indoor activities, an SPF of 30 suffices.
- Engaging in outdoor activities? Opt for SPF 50 or more.
- Regular sunscreen use is an affordable investment in skin health.
- Skin health isn't just about aesthetics; it's about overall wellbeing.
- Making sunscreen a routine can save you from future skin complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Regular daily use of SPF 15 sunscreen can reduce your risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) by about 40 percent and lower your melanoma risk by 50 percent. Help prevent premature skin aging caused by the sun, including wrinkles, sagging and age spots.
Why is sunscreen important for acne? Sunscreen is important for acne-prone individuals because the UVA and UVB rays from the sun can make areas of hyperpigmentation more noticeable and acne scars less likely to fade. It can cause further acne breakouts due to increased debris on the skin's surface.
A true skincare routine may seem complicated, but the focus should be skin protection, cleansing, moisturizing, prevention and support. While we can't prevent all signs of aging, some strategies can help protect and improve our skin.
The most serious result of forgoing sunscreen is skin cancer, but that's not the only reason to apply it. According to the Cleveland Clinic, sunburns damage the skin cells and blood vessels and can cause the skin to look older, more wrinkled, dry, discoloured, and leathery.
If you go outside without protection, you increase your risk of skin cancer. This is one of the more serious concerns of sun exposure. There are a variety of skin cancers you might develop. For example, you could develop basal cell carcinoma, or you could get melanoma.